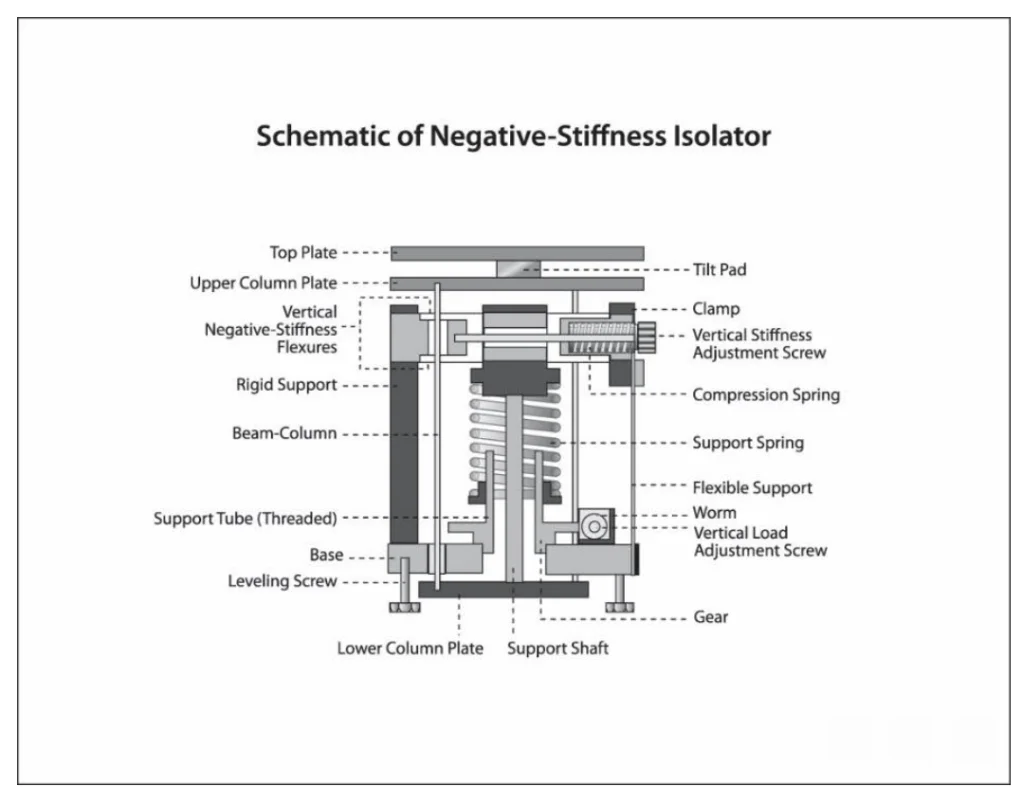
Executive Summary
Europe’s “quantum decade” is unfolding rapidly, with advances in computing, navigation, sensing and communications moving from research to real-world applications — now extending into space. And France is right at the heart of this new era. Getting there, however, will not be easy. Policymakers sound a note of caution. They warn that without strong investment in software, Europe risks lagging in the global race for quantum utility, even as hardware access improves. However, as August’s news shows, business momentum is building, highlighted by quantum’s mainstream debut at VivaTech 2025, SEALSQ’s acquisition of IC’ALPS, and Alice & Bob’s work with Inria on more efficient fault-tolerant computing. On the research front, EPFL developed new methods to simulate quantum spin liquids, while French scientists demonstrated record coherence times in a carbon nanotube qubit. Europe is positioning its ecosystem through events like Q2B Paris to align scientific progress with industrial and policy priorities.
Policy
Europe’s quantum decade extends into space
Europe – and the world – is in the midst of the ‘quantum decade’: a period in which the peculiar properties of matter that manifest at the very tiniest of scales are being transformed from mere scientific curiosities into the basis of practical technologies and products. The result? Major leaps forward in communications, navigation, computing and environmental sensing.
Why the EU needs to go hard on quantum computing software

The Allied cracking of Germany’s Enigma machine reshaped the course of World War II. Now, Europe is racing to harness a far more powerful code-breaking tool — the quantum computer, but it’s running short on the software needed to do it. In the near future, the quantum computer holds the power to impact sectors from defence, to health care, chemicals and more with hardware already more and more accessible.
Business
French Tech Wire: Quantum Computing Finds Its Mainstream Moment
Quantum computing took center stage at VivaTech 2025 last month, with NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang serving as the show’s emcee. Gone were the days of quantum being relegated to academic side sessions or tucked away in research corners. Instead, Huang said quantum is ready for its mainstream moment.
SEALSQ Corp, a company that focuses on developing and selling Semiconductors, PKI, and Post-Quantum technology hardware and software products, and its parent company, WISeKey International Holding Ltd (NASDAQ: WKEY / SIX: WIHN), a global leader in cybersecurity, digital identity, and IoT technologies, today announced that it received final approval from the French Ministry of the Economy, Finance and Industrial and Digital Sovereignty under applicable foreign investment regulations and subsequently completed the acquisition of 100% of the share capital and voting rights of IC’ALPS SAS from its current shareholders (the “Sellers”), effective August 4, 2025.
Scientists from Alice & Bob,a global leader in the race for fault-tolerant quantum computing, and Inria, France’s national institute for research in digital science and technology, have submitted a new study for peer review illustrating the most hardware-efficient method to date for producing magic states on superconducting quantum computers, a critical step toward realizing practical quantum computation.
Research
Researchers at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have made significant strides in simulating topological quantum systems, specifically a type known as quantum spin liquid. This development utilizes a novel numerical methodology, as detailed in a recent publication in Nature Physics.
Physicists still divided about quantum world, 100 years on
The theory of quantum mechanics has transformed daily life since being proposed a century ago, yet how it works remains a mystery — and physicists are deeply divided about what is actually going on, a survey in the journal Nature indicated.
The carbon nanotube gatemon qubit
Existing gatemon qubits rely on extended conductors such as epitaxial semiconductors or graphene, limiting exploration of smaller-scale quantum conductors. A French-led team of researchers integrated a single carbon nanotube into a circuit quantum electrodynamics setup, achieving gate-tunable qubit control with record coherence times of 200 nanoseconds. The study identifies charge noise as the main source of decoherence and positions carbon nanotubes as promising candidates for future quantum technologies.
Education and Events
Q2B Paris Quantum Technologies Conference, Sep 24, 2025
Q2B is Europe’s leading quantum conference, bringing together global experts, industry leaders, and policymakers to explore breakthroughs.