Insider Brief
- Q.ANT and Fraunhofer IPA signed an agreement to establish the Competence Centre Human-Machine-Interface.
- The teams will collaborate on a system to detect the finest nerve signals from muscle activity and interpret the resulting information in order to control machines and devices.
- Q.ANT plays a leading role in the field of magnetic field sensors based on quantum technology.
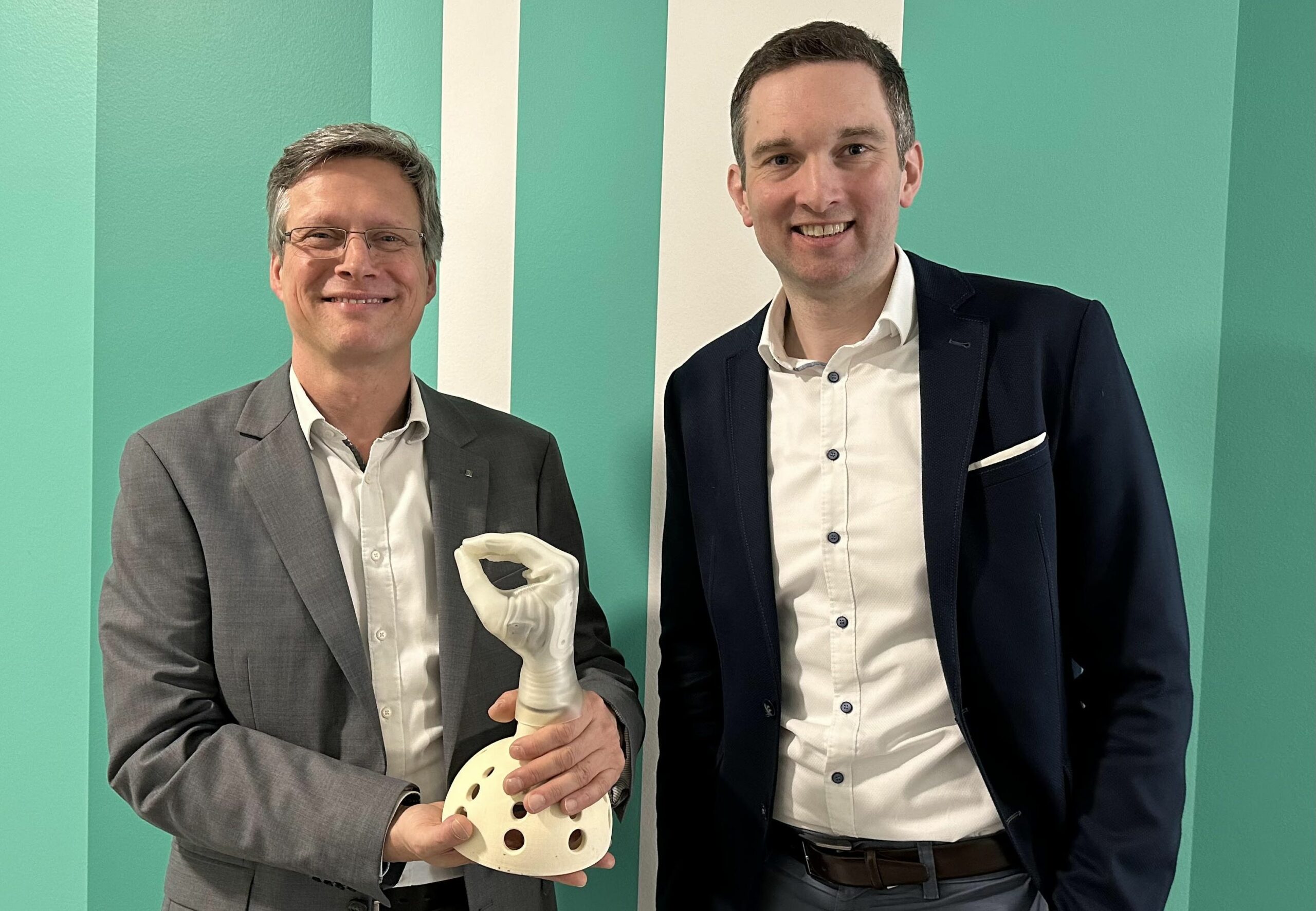
- Image: Urs Schneider from Fraunhofer IPA and Michael Foertsch from Q.ANT aim to develop innovative prosthesis control systems with this partnership.
PRESS RELEASE — The high-tech company Q.ANT and Fraunhofer IPA signed an agreement to establish the Competence Centre Human-Machine-Interface. The aim of the cooperation is to detect the finest nerve signals from muscle activity and interpret the resulting information in order to control machines and devices. This could make it possible to intuitively control hand prostheses in the future.
Q.ANT plays a leading role in the field of magnetic field sensors based on quantum technology. “The sensor from Q.ANT enables the fine sensitivities that we need for reading biosignals,” says Urs Schneider, Head of Biomechatronics Research at Fraunhofer IPA. The competence centre is based in Stuttgart and brings together around 15 experts from research and industry.
“We want to control prosthetic hands, just like healthy limbs, using neural impulses. Fraunhofer IPA brings proven expertise in this field of biomechatronics to our strategic partnership. This can be used to develop completely new applications in medical technology. We are therefore among the pioneers in this promising field of application for quantum sensor technology and are redefining the human-machine-interface,” says Michael Förtsch, CEO of Q.ANT, which specialises in photonic quantum technologies for sensing and computing.

Both cooperation partners bring many years of experience to the collaboration: Q.ANT has been developing a magnetic field sensor based on quantum technology for five years. It is characterised by its combination of sensitivity, size, and operation at room temperature. Fraunhofer IPA can draw on more than 15 years of expertise in biomechatronics and biosignal processing. The IPA specialists will characterise biosignals in order to program the corresponding algorithms that convert the sensor data into control commands for the prosthesis. The Fraunhofer Institute will also carry out the corresponding series of tests with patients, the results of which will be incorporated into the development of the prosthesis prototypes.
If you found this article to be informative, you can explore more current quantum news here, exclusives, interviews, and podcasts.