Insider Brief
- IonQ announced it achieved 99.99% two-qubit gate fidelity using its Electronic Qubit Control (EQC) technology.
- The result, demonstrated on prototype systems in IonQ’s R&D labs, is intended to form the basis for its upcoming 256-qubit systems scheduled for 2026.
- IonQ said the improved fidelity could accelerate progress toward large-scale fault-tolerant quantum computers by reducing error correction requirements and enabling more complex algorithms.
PRESS RELEASE — IonQ (NYSE: IONQ), the world’s leading quantum company, today released the technical papers that demonstrate 99.99% two-qubit gate performance, setting a new quantum computing world record.
The performance of quantum computers today is limited by the error rate of their two-qubit gates, called “two-qubit gate fidelity.” This single number largely defines quantum computing performance—measuring the accuracy of quantum operations. As fidelity improves, fewer errors must be addressed and more complex algorithms can be run.
In a landmark technical result, IonQ has achieved the world’s highest two-qubit gate performance, with fidelity exceeding 99.99%—the first and only quantum computing company to cross the “four-nines” benchmark. The demonstration released today, achieved using IonQ’s proprietary Electronic Qubit Control technology (EQC), surpasses the previous world record of 99.97% set in 2024 by Oxford Ionics, now part of IonQ.

This new world record represents a critical technical milestone that advances IonQ’s leading quantum technology roadmap. By engineering qubits with record-level fidelity, IonQ has now achieved the hardware performance required for it to scale to millions of qubits by 2030. This is a historic achievement that positions IonQ well ahead of its competitors.
IonQ’s ultra-high qubit performance accelerates the company’s path to large-scale fault-tolerant systems and unlocks major advantages:
- Error-corrected performance improves dramatically: IonQ’s unparalleled qubit performance means customers will be able to run applications with a 10¹⁰ (10,000,000,000x) performance increase over the previous gold standard of 99.9% on the same size device.*
- Complex, breakthrough use cases can be addressed: High-performing qubits enable complex algorithms that lower-performance systems simply cannot address.
- Products can be delivered faster: Fewer physical qubits are needed to build large-scale fault-tolerant quantum systems, and IonQ’s time to market decreases due to fewer errors per operation.
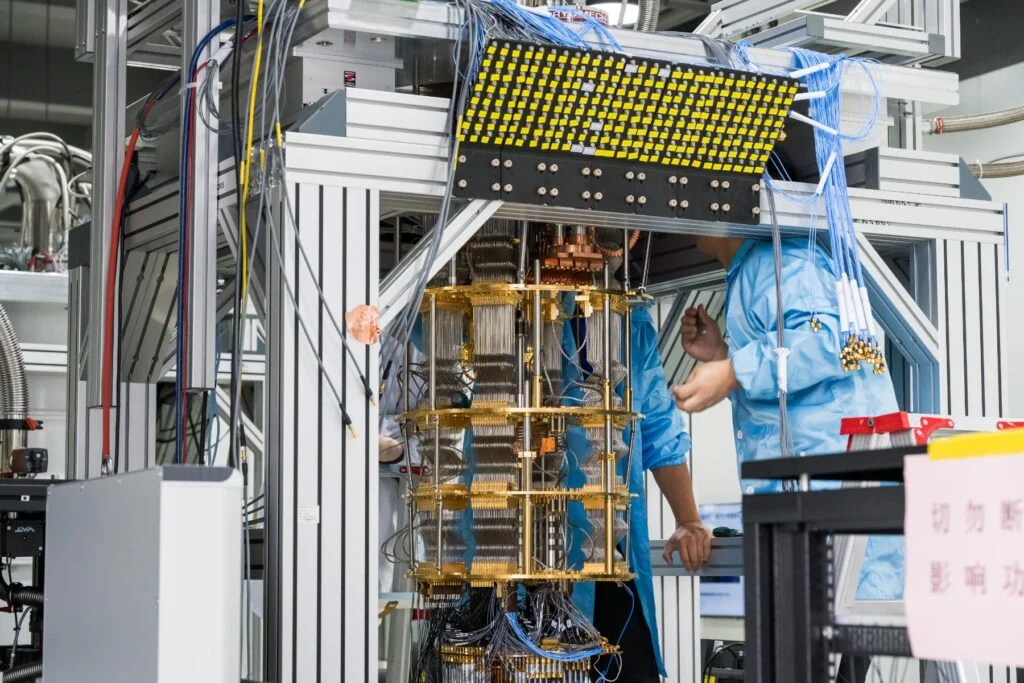
IonQ’s qubit performance result was achieved using prototypes in its R&D labs, which will form the basis for its 256-qubit systems that will be demonstrated in 2026. These devices rely on the company’s novel EQC technology, which uniquely uses precision electronics instead of lasers to control its qubits. By integrating all qubit-control components onto classical semiconductor chips, IonQ can manufacture its quantum computers via existing semiconductor fabrication—yielding systems that are easier to scale, more stable to operate, and significantly more cost-effective to build.
“Reaching four-nines fidelity is a watershed moment for IonQ’s quantum leadership,” said Niccolò de Masi, Chairman and CEO of IonQ. “This level of quantum performance has been the industry’s north star for decades and crossing it brings fault-tolerant quantum systems years closer to mass market adoption. For our global customers, it means unlocking more value from quantum computing sooner, while dramatically lowering the cost and complexity of large-scale systems.”
“This is a pivotal moment for the quantum computing industry, as we have now hit world-record quantum computing performance on mass-manufacturable technology,” said Dr. Chris Ballance, co-founder of Oxford Ionics, an IonQ company. “In exceeding the 99.99% threshold on chips built in standard semiconductor fabs, we are now on a clear path to millions of qubits whilst unlocking powerful new commercial applications sooner.”
IonQ is already delivering quantum advantage for industries in areas such as drug discovery, with a 20x speed-up in quantum-accelerated drug development announced in June this year and an up to 12 percent performance improvement compared to classical computing in computer aided engineering unveiled in March. IonQ has also announced the development of quantum applications in areas such as object detection for autonomous vehicles and artificial intelligence.
For more information about this seminal result, read more on IonQ’s blog [insert hyperlink].
For more information about IonQ’s technology and roadmap, visit www.ionq.com.
*IBM Quantum (2024). “High-threshold and low-overhead fault-tolerant quantum memory.” Nature, 627(8005), pp.778–782. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07107-7