Insider Brief
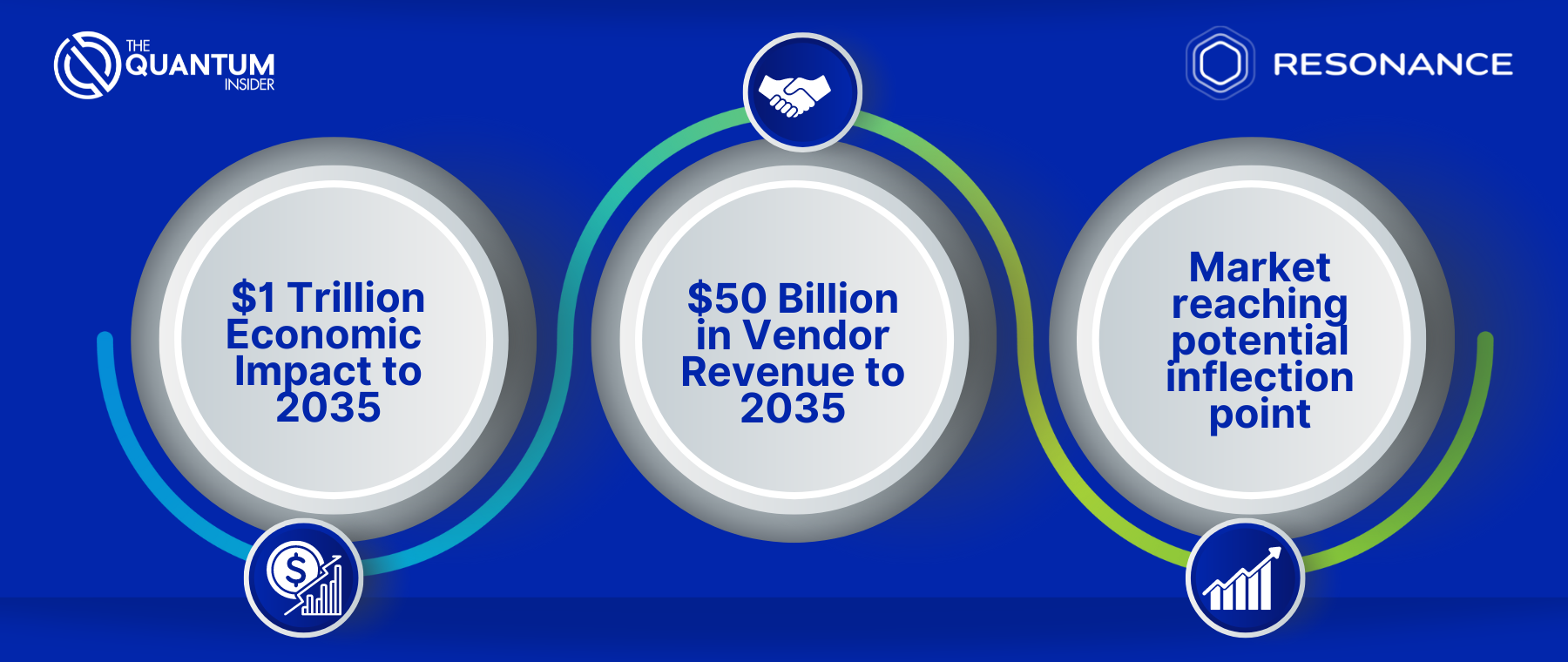
- Economic Impact: A new report from The Quantum Insider forecasts that quantum computing will contribute $1 trillion in value creation by 2035.
- Vendor Revenue: Quantum computing vendors expected to generate $50 billion in revenue by 2035.
- Job Creation: Quantum computing will create an estimated 840,000 new jobs by 2035, with 250,000 by 2030.
The global quantum computing market could add a total of more than $1 trillion to the global economy between 2025 and 2035, according to a new analysis from The Quantum Insider, the leading source of market intelligence on the quantum technology landscape. Vendors are expected to capture $50 billion of revenue over this period.
This forecast points to the significant economic potential unlocked by quantum computing and reflects the growing confidence in quantum technologies as they edge ever closer to mainstream adoption, said Alex Challans, CEO of The Quantum Insider. “Quantum computing is set to unlock material value across multiple trillion-dollar industries,” Challans said. “We expect this to drive material economic growth and job creation in regions which lean into supporting the technology.”
Quantum Market Growth: A Closer Look
The Quantum Insider’s recent report, underpinned by proprietary data and stakeholder interviews, assesses the quantum market from two perspectives:

Firstly, the value creation unlocked looks at the incremental revenue and cost savings driven by quantum computing. This is estimated as a cumulative $1 trillion of value creation through to 2035.
Secondly, the revenue accrued to quantum computing vendors through hardware sales, QCaaS and professional services. This is estimated at a cumulative $50 billion of revenue through to 2035.
Value creation
The report estimates that quantum computing will unlock a cumulative $1 trillion of value creation for end users through to 2035.
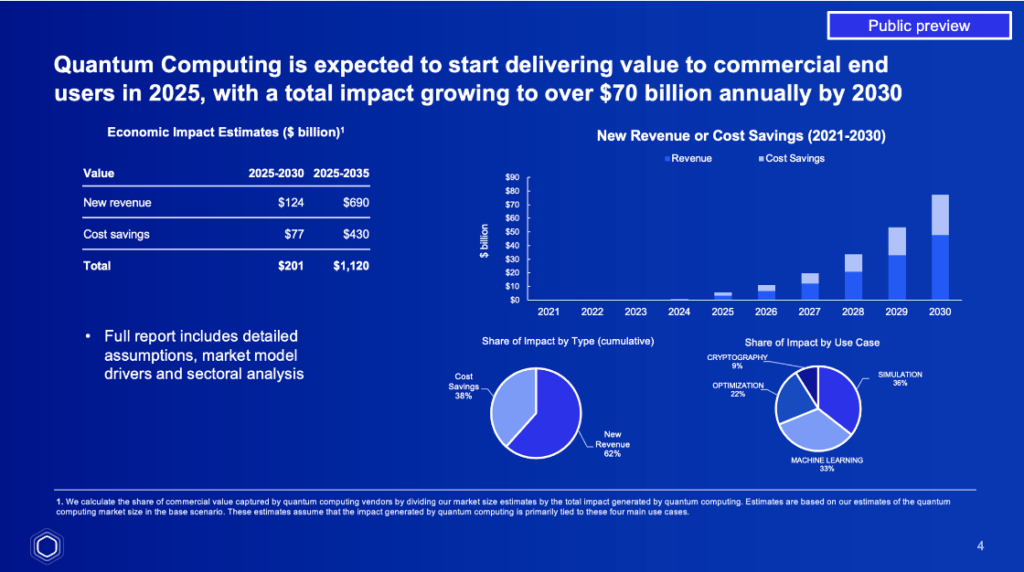
Industries set to benefit the most from quantum computing include finance, defense, life sciences, telecommunications, and manufacturing. The finance and defense sectors are expected to experience the greatest economic impact, with projected annual contributions of $20 billion and $10 billion, respectively, by 2030. Quantum computing’s ability to solve certain complex problems faster and more efficiently than classical computers makes it a valuable asset in these sectors.
According to the report, the economic impact of quantum computing will not be evenly distributed across the globe. The report highlights that countries such as the USA, the UK, Germany, France, China and Japan are currently positioned to capture much of the value created by quantum computing by 2035. Substantial public and private investments in these regions have accelerated the development and deployment of quantum technologies.
Quantum computing is not only about technological advances; it’s also expected to be a significant driver of job creation. The report estimates that the quantum sector will generate approximately 250,000 new jobs by 2030, jumping to 840,000 by 2035. Because quantum computing is expected to play a broad role in economic development, the jobs will span a range of industries, from software development and systems integration to research and development.
The analysts based their job creation estimates on projected QC investments, along with two alternative methods: first, estimating jobs created per dollar invested, and second, estimating jobs created per dollar generated in new revenue. These were triangulated to the trajectory of other sectors such as High Performance Computing (HPC) and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Vendor revenue
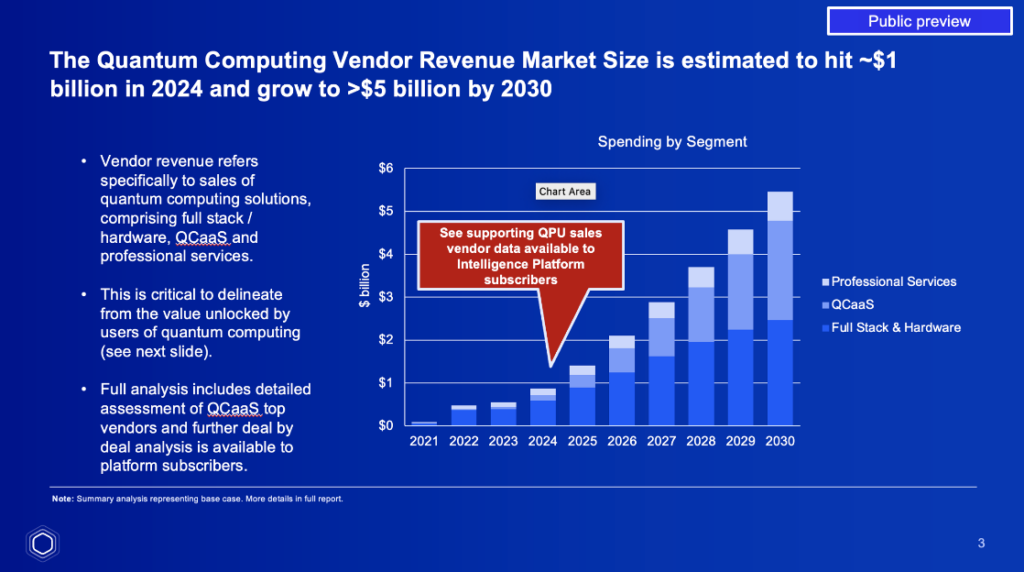
The report indicates that the market size for quantum computing vendors will grow substantially in the next five years. Starting from an estimated $1 billion in 2024, the market for quantum hardware and software is expected to expand to approximately $5 billion by 2030 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36% as a base case. More bullish scenarios outlined by The Quantum Insider place the opportunity at $15 billion annual revenue by 2030.
According to Challans: “Quantum computing is transitioning from the lab to the real world. We’re seeing the early stages of an industry that will redefine everything from cybersecurity to material science.”
The report, underpinned by vendor-level sales data, divides the quantum computing market into three primary segments, each playing an important role in this industry’s expansion:
- Full Stack and Hardware: This segment, currently the largest, accounts for nearly 70% of the market. It encompasses the sale of quantum computers, hardware components and comprehensive solutions offered by various vendors. While it will continue to grow, its share of the market is expected to decrease as other segments expand.
- Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS): QCaaS is projected to see the most significant growth, driven by increasing commercial adoption and the expansion of cloud-based quantum services by major players like AWS, Google Cloud and Azure. By the end of the decade, QCaaS is expected to represent over 40% of the quantum computing market. Back in 2021, The Quantum Insider built an initial market model estimating the QCaaS market could reach up to $26 billion by 2030, including both the vendor revenue and value unlocked for vendors. This latest analysis builds on this initial methodology to include detailed data on QPU usage and more granular information on use cases and proof of concept rollouts.
- Professional Services: This segment includes consulting, research and training services related to quantum computing. While currently comprising about 17% of the market, its relative importance is expected to diminish as QCaaS becomes more prominent and as quantum technologies mature.
“We’re witnessing a shift in how quantum technologies are accessed and used,” Challans added. “The growth of QCaaS is particularly exciting because it lowers the barrier to entry for businesses that want to experiment with quantum solutions without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware. This type of accessibility means that companies that were not able to participate in the market, will suddenly become active players, adding not only to the revenue stream going into quantum, but likely serve as a source of that cost savings and innovation.”
Strategic implications
As the quantum computing industry grows, the report suggests that stakeholders—including companies, investors, and governments—must be strategic in their investments to capitalize on the opportunities this emerging technology presents. Those who invest early and strategically in quantum technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
“Quantum computing is not a future technology; it’s a now technology,” says Challans. “The insights from our report make it clear that those who act quickly and wisely in this space will be the ones who define its future.”
Readers can access the full report through a subscription to The Quantum Insider’s Intelligence Platform. Learn more at www.thequantuminsider.com/data. The supporting market model is available for purchase by contacting through this form.
About The Quantum Insider and Resonance
Resonance is the leading provider of market intelligence across deep tech verticals, through platforms including The Quantum Insider, Space Impulse, Digital Twin Insider, Climate Insider, and AI Insider. Resonance delivers actionable insights that drive innovation and smart investments. With a focus on strategic integration of breakthrough technologies, Resonance serves clients ranging from startups to national governments with its SaaS intelligence, strategic advisory, and marketing services.