By Yuval Boger, Chief Commercial Officer, QuEra
As quantum computing continues to advance, its potential to revolutionize various industries is becoming increasingly apparent. While the field has made remarkable strides, surpassing even the expectations of many experts, significant challenges remain. A recent survey of nearly 1,000 experts conducted by QuEra in June 2024 sheds light on the current stage of quantum computing development, the technical hurdles that need to be overcome, and the ethical considerations that must guide its future.
The Quantum Frontier is Accelerating
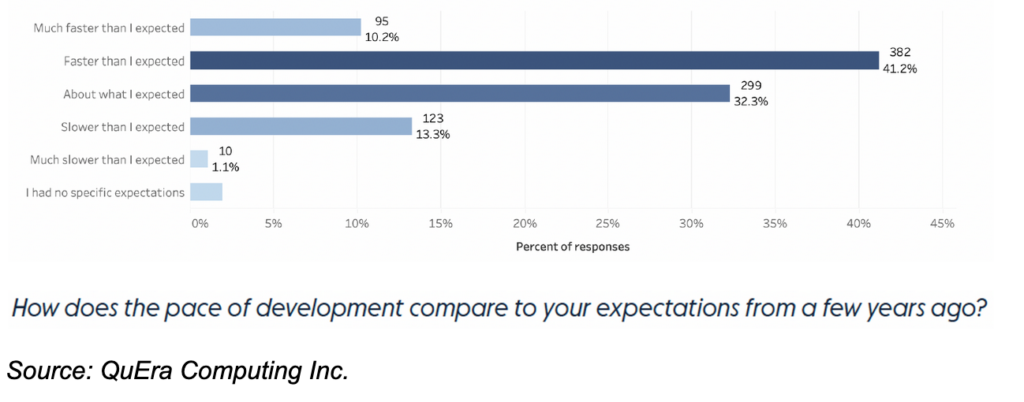
The quantum computing industry is moving faster than most people predicted just a few years ago. According to the survey, 51.4% of respondents believe that the pace of development was faster or much faster than their expectations. This rapid growth reflects the substantial investments and research efforts that have fueled quantum advancements. As quantum computing edges closer to practical applications, the excitement surrounding its potential is palpable.

Technical Challenges Remain
Despite this rapid progress, quantum computing is not without its challenges. The survey reveals that scalability (33.1%) and error correction (30.9%) are the most pressing technical issues facing the field. These challenges are critical to advancing quantum computing beyond its current limitations.
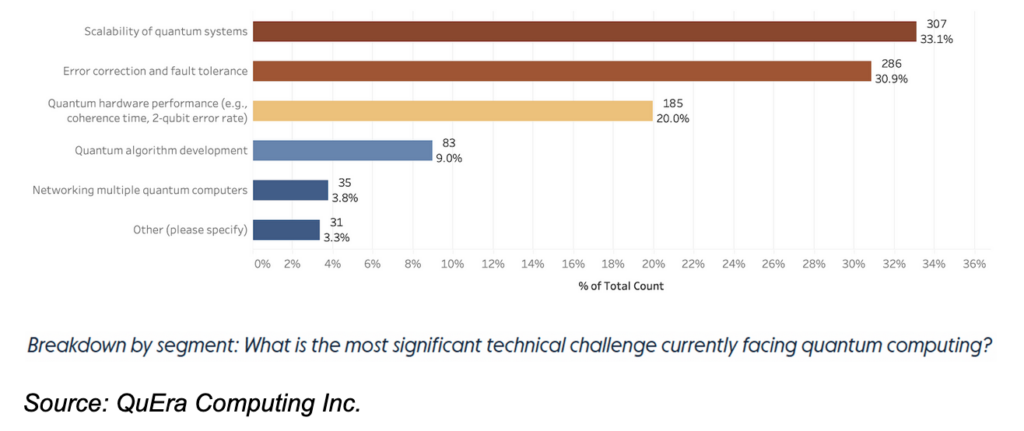
For quantum computing to reach its full potential, scalability must be addressed. The ability of quantum systems to handle larger, more complex problems as the technology matures is paramount. Currently, quantum computers are limited by the number of qubits they can effectively manage, which restricts their capability to solve real-world problems at scale.
Equally important is the need for robust error correction and fault tolerance. Quantum systems are highly sensitive to external disturbances, making them prone to errors. As quantum computing inches closer to practical use, developing effective error correction methods will be crucial for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of quantum computations.
Navigating Ethical Waters
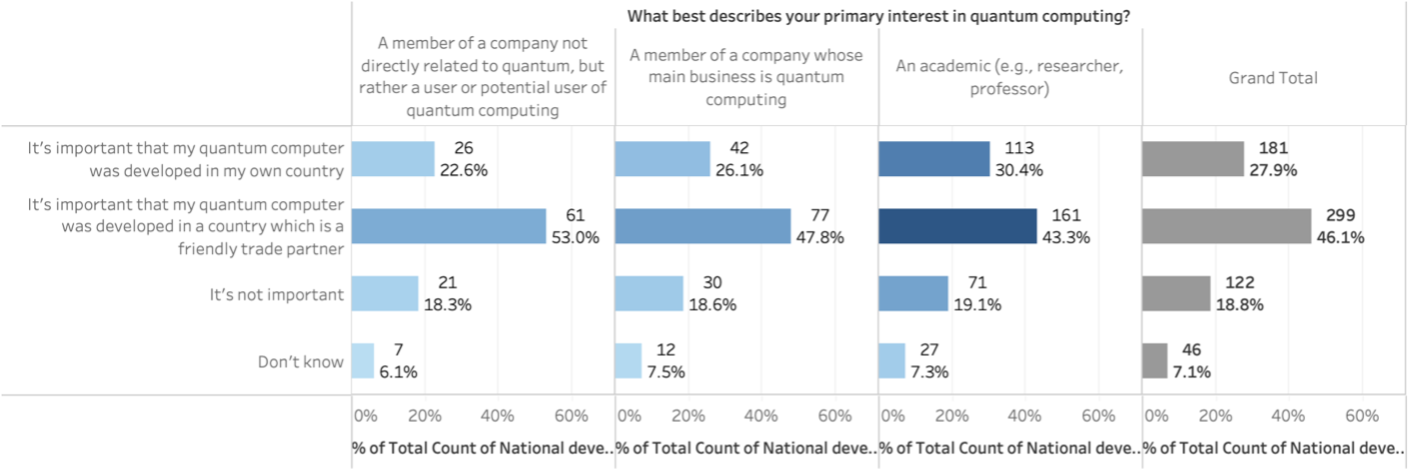
As quantum computing technology advances, it brings with it a host of ethical considerations that must not be overlooked. Privacy concerns are at the forefront, particularly with the potential for quantum computers to break current encryption methods, putting sensitive data at risk. The survey indicates that 67.2% of respondents view privacy and security as top ethical priorities.
Another critical issue is equity in access to quantum technologies. Without careful consideration, the benefits of quantum computing could be disproportionately distributed, exacerbating global inequalities. Ensuring that all countries and communities have access to this transformative technology is essential for fostering global innovation and avoiding conflict.
The environmental impact of quantum computing is also a growing concern. The energy required to operate quantum computers, especially in maintaining ultra-cold temperatures for certain quantum processes, is significant. As the technology scales, developing more energy-efficient quantum systems will be key to minimizing its environmental footprint.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Quantum Computing
The quantum computing community remains optimistic about the future, with many believing that the technology will surpass classical computing for certain workloads in the near future. According to the survey, 37.9% of respondents expect quantum computing to become a superior alternative within the next 1-5 years, while 37.1% believe this could happen within 6-10 years.
This optimism reflects a growing confidence in quantum computing’s ability to tackle challenges that classical computers cannot. However, the timeline for widespread adoption will depend on continued advancements in hardware, software, and algorithms.
Balancing Progress with Responsibility
Quantum computing is on an accelerated trajectory, with significant technical challenges that need to be addressed. As the technology continues to evolve, ethical considerations such as privacy, equity, and environmental impact must remain central to the conversation. The next few years will be critical in determining how quickly and effectively quantum computing can transition from a promising research area to a practical tool with a wide array of applications. By balancing rapid progress with thoughtful consideration of its broader implications, we can ensure that quantum computing develops in a way that is not only technically sound but also socially responsible.
Access the full report at https://quera.link/repweb