Insider Brief
- Biotech company legacy Novozymes (now Novonesis) has collaborated with Danish quantum company Kvantify to perform the world’s first calculation of an enzymatic reaction on a quantum computer.
- The team said the experiment shows how quantum computers and classical computers will work together in the future.
- This calculation can potentially save large amounts of time and resources for experiments that would have to be carried out in other ways.
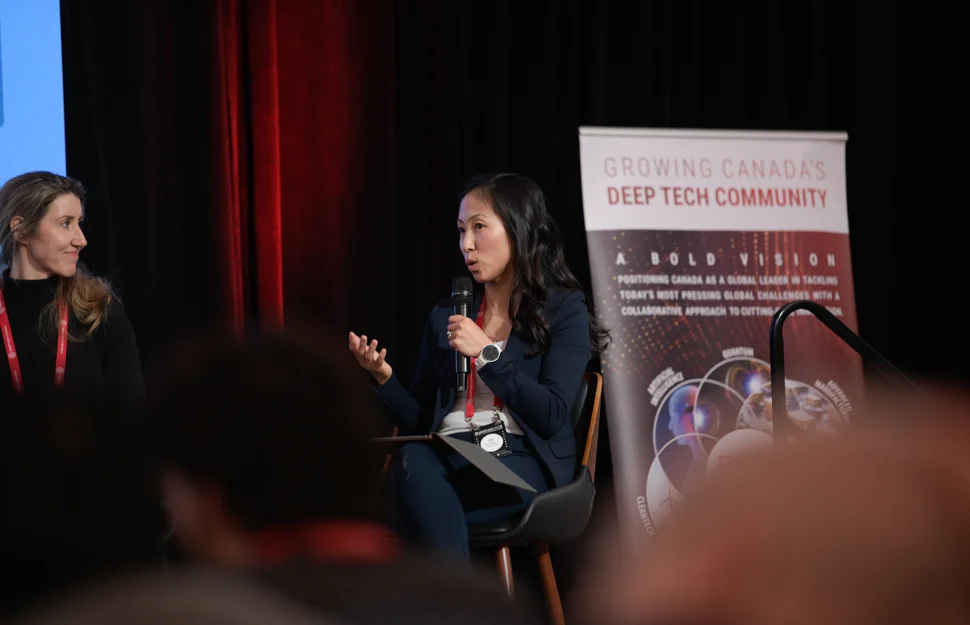
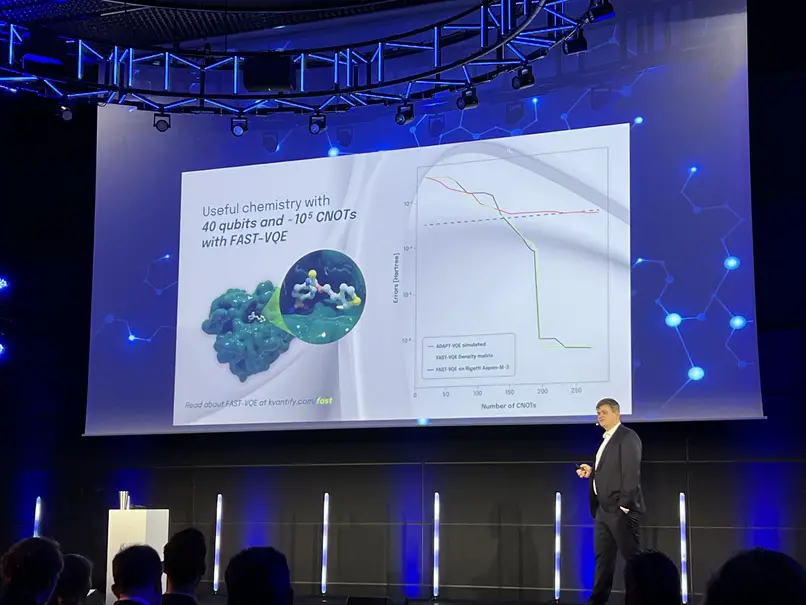
- Image: Hans Henrik Knudsen, co-founder, and CEO of Kvantify, on stage talking about the algorithm (FAST-VQE) that has made the Novonesis enzyme calculations possible.
PRESS RELEASE — Today, global biotech company Novonesis and Danish quantum computing company, Kvantify, announced that they have performed the world’s first calculation of an enzymatic reaction by combining classical and quantum computers. In this way, the critical part of the reaction has been calculated with a quantum computer, and it helps to show the way quantum computers and classical computers will work together in the future.
“This is a remarkable achievement that sets a new standard for the utilization of quantum computers worldwide. At Kvantify, we do computational analyses of difficult real-world problems, so we are proud to show the potential of this type of problem-solving. Enzymes work through reactions at the quantum level, making them a natural use-case for quantum computing, and that is exactly our mission. We identify where quantum computing can make the biggest difference and help our partners build the necessary software solutions. This collaboration shows one of the many opportunities for quantum computing in the biotech and pharma industry, and we are extremely pleased that Novonesis sees the potential of the technology,” says Hans Henrik Knudsen, co-founder, and CEO of Kvantify.
The enzyme used is carbonic anhydrase, which might not ring a bell to many. However, the enzyme catalyzes the conversion of CO2 and water into carbonic acid, a crucial process for many organisms, among other things, regulating blood pH and transporting carbon dioxide in the body, and can be used industrially for CO2 capture. By using this type of calculation, you can potentially save large amounts of time and resources for experiments that would have to be carried out in other ways.

A partnership that shapes the future Kvantify’s new quantum algorithm “FAST-VQE” makes it possible to characterize the reaction of carbonic anhydrase, which can accelerate useful knowledge for the benefit of Novozymes: “With this kind of calculation and subsequent analysis of how enzymes behave during catalysis, we can gain a deeper understanding of fundamental biological processes. We will gain insights that can improve the efficiency of our existing enzyme products. This collaboration is an important step in exploring the potential of quantum computing in the future of enzyme research, and the innovation being created through this collaboration has the potential to strengthen our position as a leader in providing sustainable bio-solutions” says Lars Olsen, senior department manager at Novozymes.
For more market insights, check out our latest quantum computing news here.