Insider Brief
- Research teams report two experiments showed a marked improvement in computing time requiring a smaller memory footprint using quantum computing techniques.
- The team adds that the results may help pave the way for their use in real-world applications in the valuation of derivatives.
- Researchers from Crédit Agricole CIB, Pasqal and Multiverse Computing conducted the studies.
PRESS RELEASE — Crédit Agricole CIB and European technology leaders Pasqal and Multiverse Computing report conclusive results on two proofs of concept using quantum computing in real-world situations.
These two experiments, initiated in June 2021 by Crédit Agricole CIB, aimed to evaluate the contribution of an algorithmic approach inspired by quantum computing, and the potential of quantum computers, in two areas: the valuation of financial products, and the assessment of credit risks.
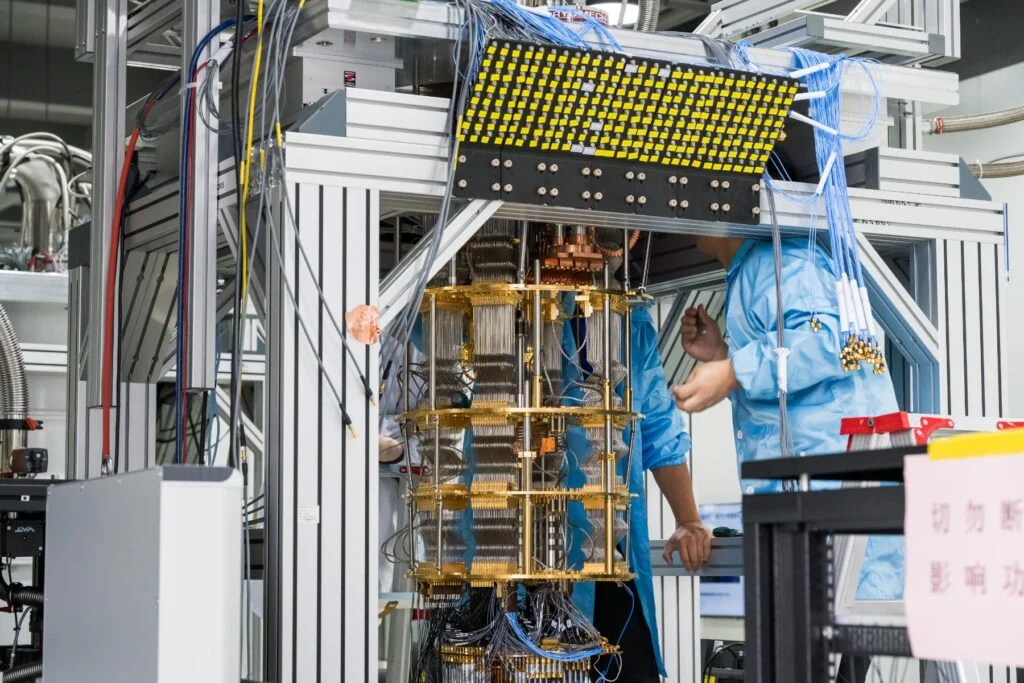
The bank partnered with French company Pasqal, a leader in the manufacture of quantum computers in Europe, and the Spanish company Multiverse Computing, which specializes in quantum and quantum-inspired algorithms, which can run on conventional computer systems.

Experiment on the valuation of derivatives in capital markets with Multiverse
The goal of this experiment was to assess the performance gain offered by quantum computing in the valuation of derivatives. Recent research has shown the benefit of neural networks for this type of calculation. Yet, in several cases, these neural networks are difficult to use because they are too resource intensive in terms of memory and suffer from lengthy processing times. However, algorithmic techniques inspired by quantum computing can be used to optimise the speed and memory required for this training phase, leading to faster valuations and more accurate risk assessments.
Experiment on the anticipated downgrade of counterparties’ financial rating with Pasqal and Multiverse
The goal of this experiment was twofold: first, to measure a quantum computer’s ability to solve a concrete problem, given the current state of technology. Second, to assess the change in performance depending on the number of qubits used. The bank chose a production use case, providing a real point of comparison: the anticipation of a counterparty credit rating downgrade over a 6 to 15-month period. Through conventional computer technology and heuristics, good results can be achieved. However, these methods do not work for all problems, and there is no guarantee that the results obtained will be close to the ideal solution. Using quantum parallelism, in theory, makes it possible to find optimum solutions more efficiently.
Both experiments successful
The two experiments took place over a year and a half and were very successful. A marked improvement in computing time requiring a smaller memory footprint was measured using quantum computing techniques, paving the way for their use in real-world applications in the valuation of derivatives. For the quantum computer, the chosen problem was tackled under real-world conditions. With a quantum processor of only 50 qubits, the results obtained are as accurate as the results in production. Our projections indicate that this performance could be bettered at 300 qubits, a power that should be available industrially in 2024.
Ali El Hamidi, the project’s sponsor at Crédit Agricole CIB, says: “These two Proofs of Concept demonstrated the potential and reality of quantum computing for finance, despite these technologies still being in their infancy. We took advantage of this initiative to start developing the internal skills to prepare for a technological breakthrough which, if it happens, will have a direct and decisive impact on competitiveness in our sector.”
Georges-Olivier Reymond, President of Pasqal, says: “This is the most instructive experiment carried out in the industry so far, offering concrete comparisons for the first time, launching a new era for quantum computing. One of the results is that the tipping point is not that far away, probably less than two years, and that it is therefore urgent for users to quickly adopt these new methods, as Crédit Agricole CIB has done. We thank our partners, Crédit Agricole CIB and Multiverse for this great success.”
Enrique Lizaso, CEO of Multiverse Computing, says: “With our leading Singularity SaaS solution, we are helping organizations solve problems with the quantum computers available to us today. This collaboration with Credit Agricole CIB, and with Pasqal for the quantum part, has clearly demonstrated that economic advantages are possible today through quantum-inspired and quantum solutions.”
Link towards a research paper on credit risk management s : [2212.03223] Financial Risk Management on a Neutral Atom Quantum Processor (arxiv.org)
Link towards a research paper on the capital markets: [2208.02235] Quantum-Inspired Tensor Neural Networks for Partial Differential Equations (arxiv.org) and [2212.14076] Quantum-Inspired Tensor Neural Networks for Option Pricing (arxiv.org)
If you found this article to be informative, you can explore more current quantum news here, exclusives, interviews, and podcasts.