Go East
We all know that when cutting-edge technology comes about, it’s the usual suspects that get their houses in order first. By this declaration, I mean the US, Russia, France, the UK, Germany, and Japan. There are others, too, of course, like China, whose extraordinary growth over the last thirty years has transformed it into a technological juggernaut that will likely overtake the US by the end of the decade, especially regarding quantum technologies.
Because when it comes to government investment in quantum research, the Americas, EMEA and APAC are streets ahead of the rest, which is no surprise really.
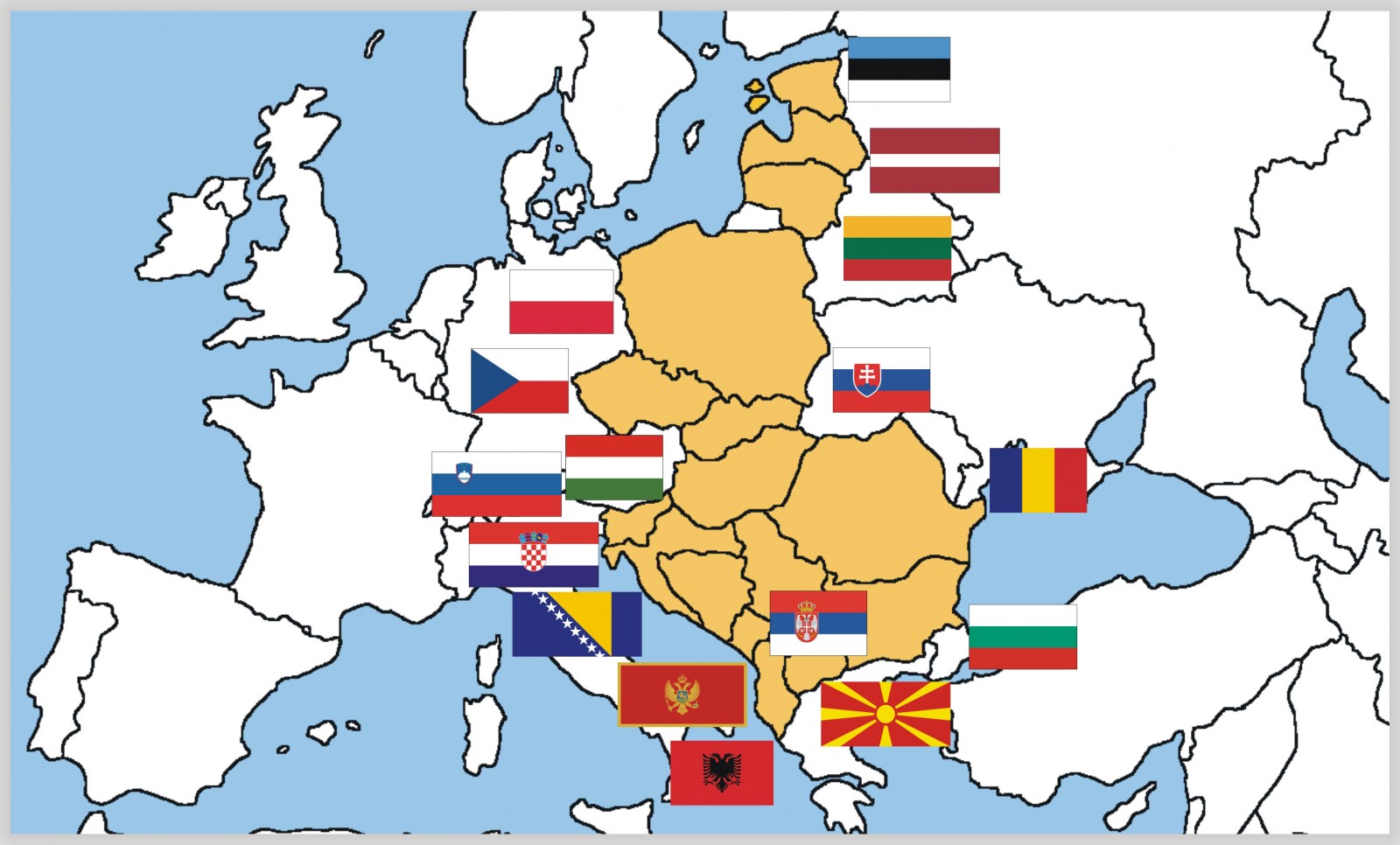
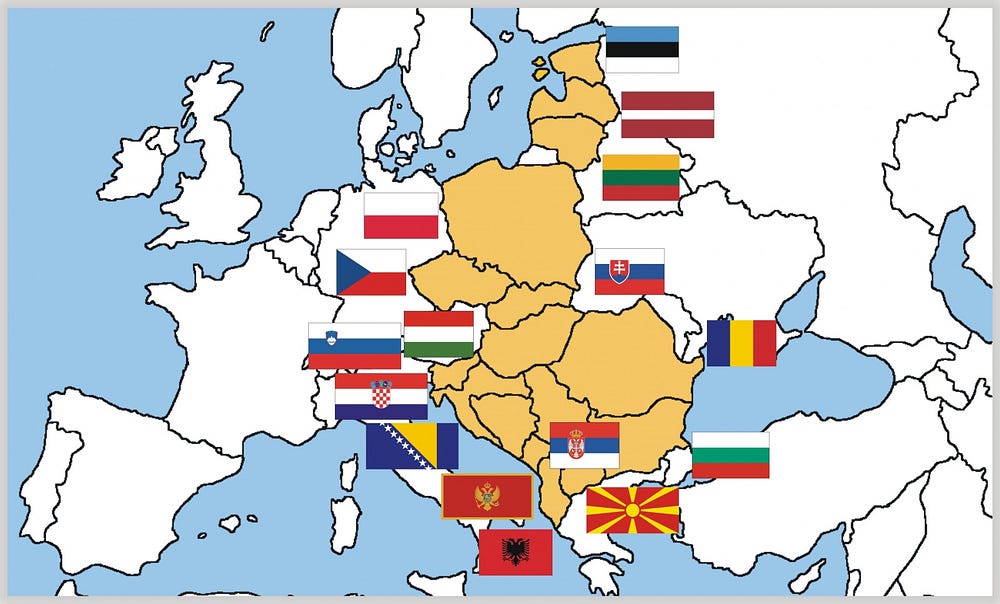
In Europe, the western countries are leading in this though other states, particularly the EU members which were once part of the former Eastern bloc (CEE), have their own projects ongoing also, though with far less funding available, as would be expected.
To highlight this achievement, TQD will now take a look at 11 of those CEE countries that, though still lacking a unified, government-backed plan, have at least some projects and partnerships in place within the scope of quantum technologies.

1. Bulgaria

Tucked away in the southeastern Balkan region, Bulgaria has several institutions that are active participants in the EU Quantum Flagship while the Bulgarian National Science Fund (BNSF) is a partner in QuantERA. A signatory on the EuroQCI declaration, a major public stakeholder is the Bulgarian Science Fund (NSFB).
2. Croatia

Like its Balkan neighbour Bulgaria, Croatia is an engaged member of the Quantum Flagship Quantum Community Network and the Croatian Science Foundation (HRZZ) is a partner in QuantERA. Also a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration, the Croatian Science Foundation is a major public stakeholder.
3. Czech Republic
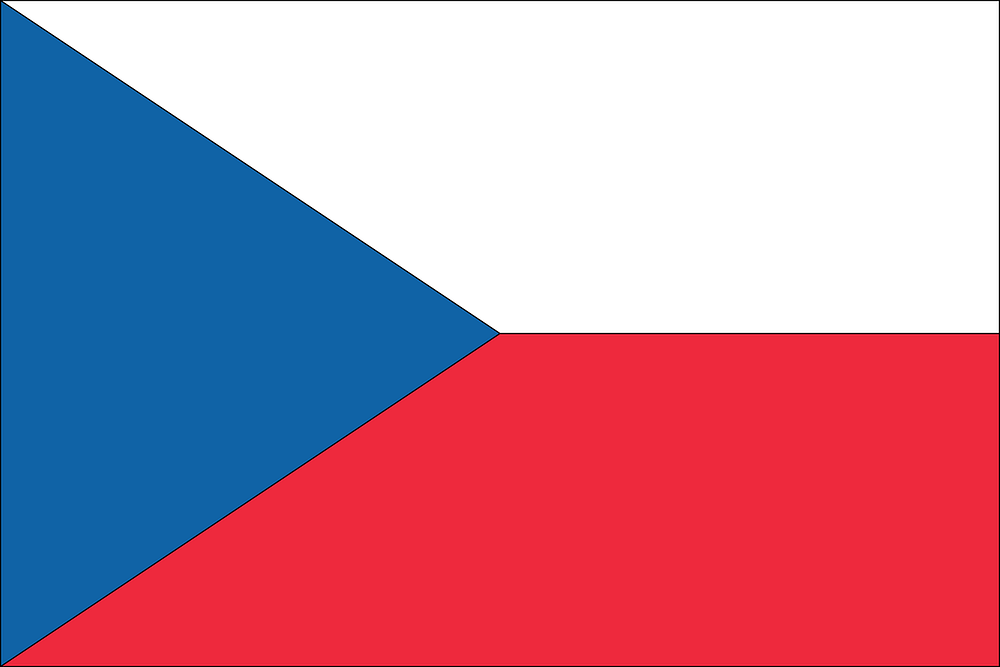
In the heart of Europe, the Czech Republic has several institutions participating in the EU Quantum Flaghship and OpenQKD. The Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports, meanwhile, is a partner in QuantERA. The country is a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration, too.
4. Estonia

One of the most technologically advanced countries in Europe, the small Baltic nation of Estonia is an active participant in a number of international quantum partnerships, for example, the EU Quantum Flagship.
5. Hungary

This central European country is busier than it should be in quantum tech considering its size. Its national quantum strategy, called the Hungarian National Quantum Technology Programme (HunQuTech), has been established to connect Hungary to the developing European quantum internet, help the country’s researchers compete with the rest of the continent in quantum technology and improve prospects for the training of quantum technology engineers and researchers within the country.
The HunQuTech consortium, with a strong focus put towards quantum communication and cryptography, brings together universities, research institutes and industry players and is responsible for the program’s implementation.
Similar to other countries already mentioned, Hungary has experts involved in the Quantum Flagship Quantum Community Network. The Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office, meanwhile, is a partner in QuantERA.
Hungary is also a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration, with another major public stakeholder being the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (NRDI).
6. Lithuania

Another Baltic state, Lithuania has experts on the Quantum Flagship Quantum Community Network while the country is a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration.
7. Latvia

Like Estonia and Lithuania, Latvia is one of the three small Baltic nations. An active participant in several international quantum partnerships, Latvia is a member of the EU Quantum Flagship. The Latvian State Education Development Agency (VIAA) is a partner in QuantERA and the country’s only public stakeholder in quantum tech to date.
8. Poland

The richest and most populous country in the CEE, Poland, unsurprisingly, is involved in numerous initiatives within the remit of QIS. With experts on the EU Quantum Flaghship and OpenQKD, the Polish National Science Centre (NCBR) is the coordinator of QuantERA and the National Centre for Research and Development (NCN) is a partner. Like the rest mentioned, Poland is a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration.
Other major public stakeholders include the Ministry of Science and Higher Education and the Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Centre (affiliated with the Polish Academy of Sciences).
9.Romania

Skirting the Black Sea, Romania is another country that is a member of the Quantum Flagship Quantum Community Network and on the Strategic Advisory Board, a major public stakeholder is the Romanian Executive Agency for Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation Funding also happens to be a partner in QuantERA. The country is a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration.
10. Slovenia

Slovenia is a small nation that used to be part of Yugoslavia along with Croatia. Active in several international quantum partnerships, Slovenian institutions are participants in the EU Quantum Flagship. One QuantERA partner is the Slovenian Ministry of Education, Science and Sport. Slovenia is yet another signatory on the EuroQCI declaration.
11. Slovakia

A part of Czechoslavakia along with the Czech Republic until both gained their independence in 1993, Slovakia’s coordinated national quantum strategy, the Slovak National Research Platform for Quantum Technologies (QUTE.sk), was set up to nurture and expand quantum technologies for the next generation of experts in quantum information structures and metrology, quantum communication, quantum simulations, and quantum/postquantum cryptography amongst others.
Under the QUTE.sk umbrella is iQUTE, a virtual research institute covering all the research activities on the main platform QUTE in the area of quantum technologies. Its goal is to create internationally competitive and sustainable research programs.
Slovakian scientists and researchers are on the Quantum Flagship Quantum Community Network and Strategic Advisory Board. In addition, the Slovak Academy of Sciences is a partner in QuantERA and, like all the others listed, is a signatory on the EuroQCI declaration.
Have we missed any out or got something wrong? If so, don’t hesitate to contact us at hello@thequantuminsider.com.
The Quantum Insider (TQI)

If you found this article to be informative, you can explore more current quantum news here, exclusives, interviews, and podcasts.